SOCRATES: Text-based Human Search and Approach using a Robot Dog
Our paper got accepted at International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), 2024.
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a SOCratic model for Robots Approaching humans based on TExt System (SOCRATES) focusing on the human search and approach based on free-form textual description; the robot first searches for the target user, then the robot proceeds to approach in a human-friendly manner. In particular, textual descriptions are composed of appearance (e.g., "wearing white shirts with black hair") and location clues (e.g., "is a student who works with robots"). We initially present a Human Search Socratic Model that connects large pre-trained models in the language domain to solve the downstream task, which is searching for the target person based on textual descriptions. Then, we propose a hybrid learning-based framework for generating target-cordial robotic motion to approach a person, consisting of a learning-from-demonstration module and a knowledge distillation module. We validate the proposed searching module via simulation using a virtual mobile robot as well as through real-world experiments involving participants and the Boston Dynamics Spot robot. Furthermore, we analyze the properties of the proposed approaching framework with human participants based on the Robotic Social Attributes Scale (RoSAS).
Proposed method
The problem is separated into search and approach phases.
Assumption and Input of the System
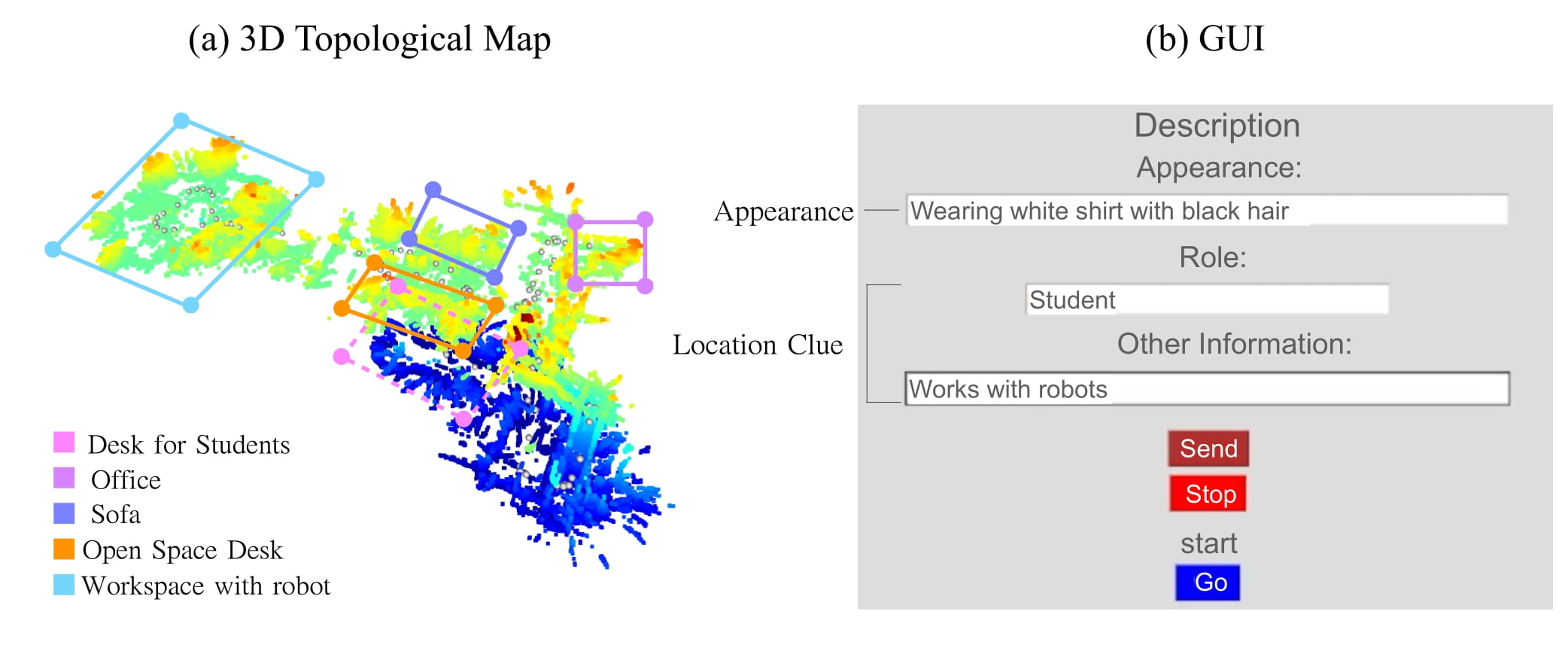
Human Search Socratic Model
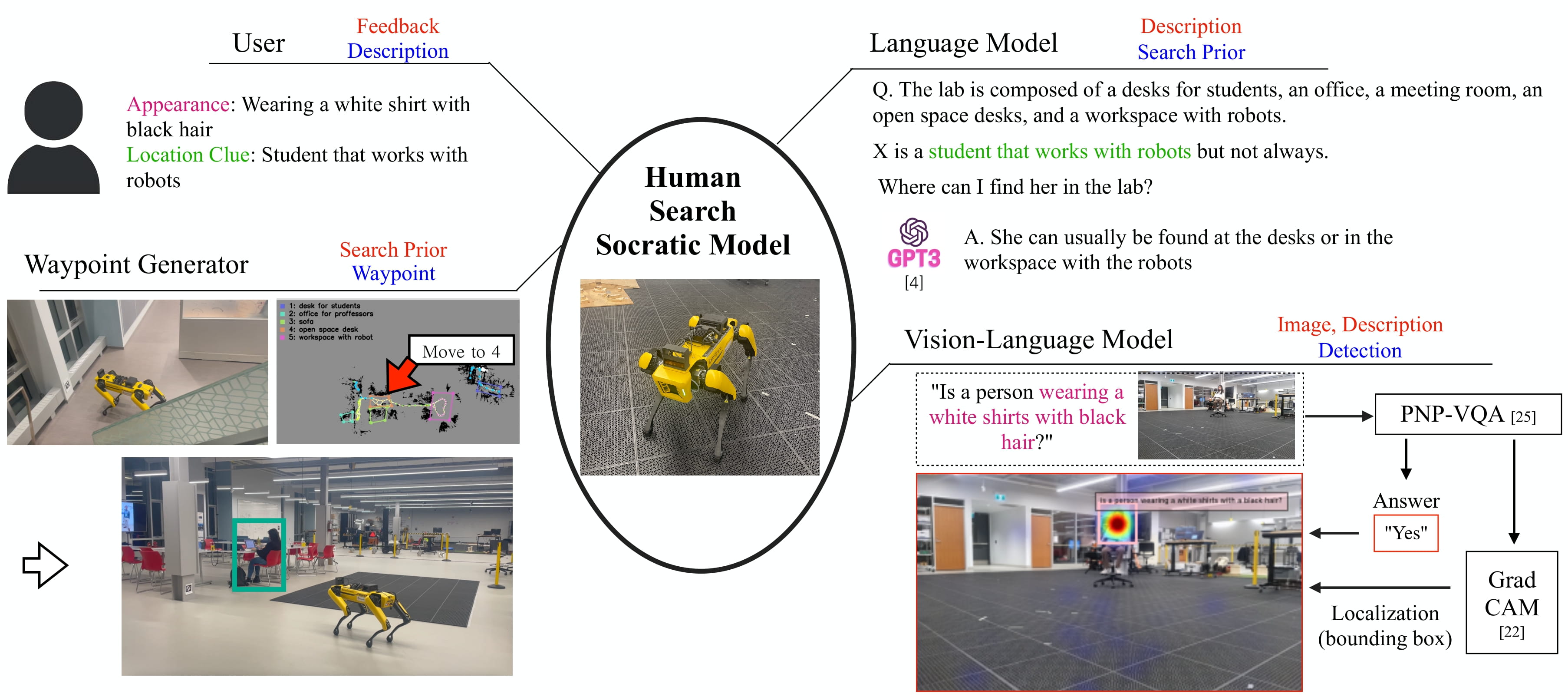
The Human Search Socratic Model is composed of three key components: a large-language model, a vision-language model, and a waypoint generator. The large-language model takes the description of a target person and estimates the search prior, whereas the vision-language model processes images and descriptions to localize the target person. Lastly, the waypoint generator commands the robotic actions with the search prior and the detection results.
Hybrid Learning Based Human Approach
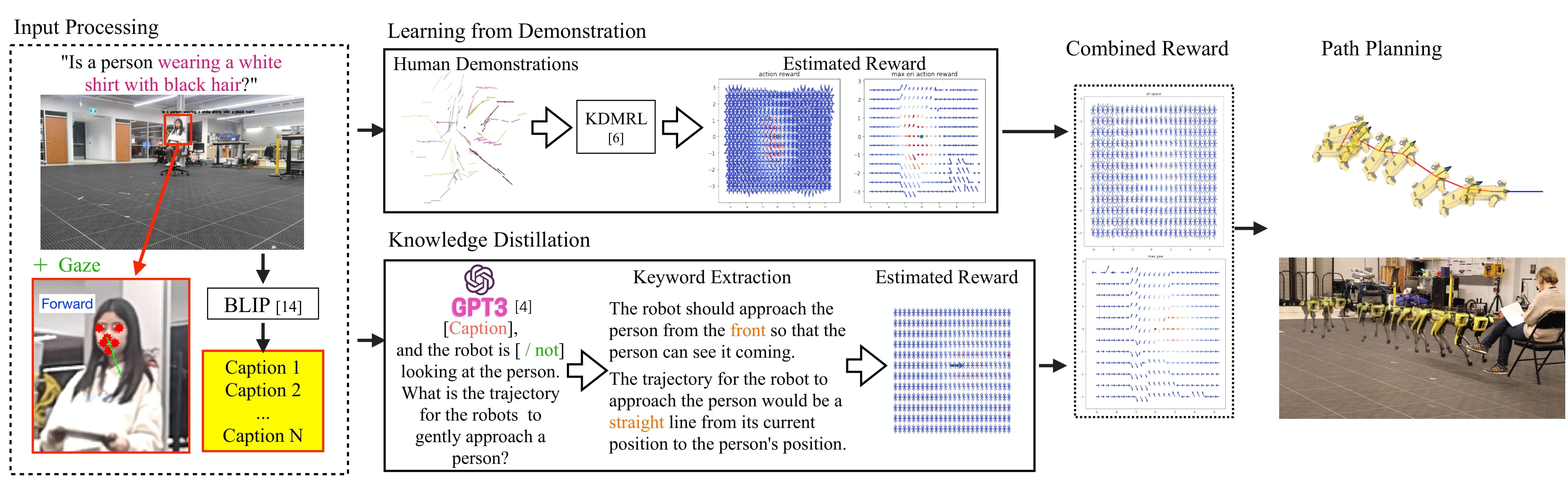
We propose a hybrid learning-based framework for generating a cordial approach motion to a target person. Target-friendly approach motions are an essential part of the "human search and approach" task since the robot has to move to a reachable position within the range of the target person without appearing threatening or distracting him/her. The proposed hybrid learning-based framework consists of two different modules: learning from demonstration (LfD) and knowledge distillation. Both modules estimate the reward function of the state space for a confiding approach trajectory and are combined to a final reward function. Next, the path planner conducts cost-aware planning based on the estimated reward function and sends actions (velocity commands) to the robot.
Demonstration
Experiment
Environment Setting
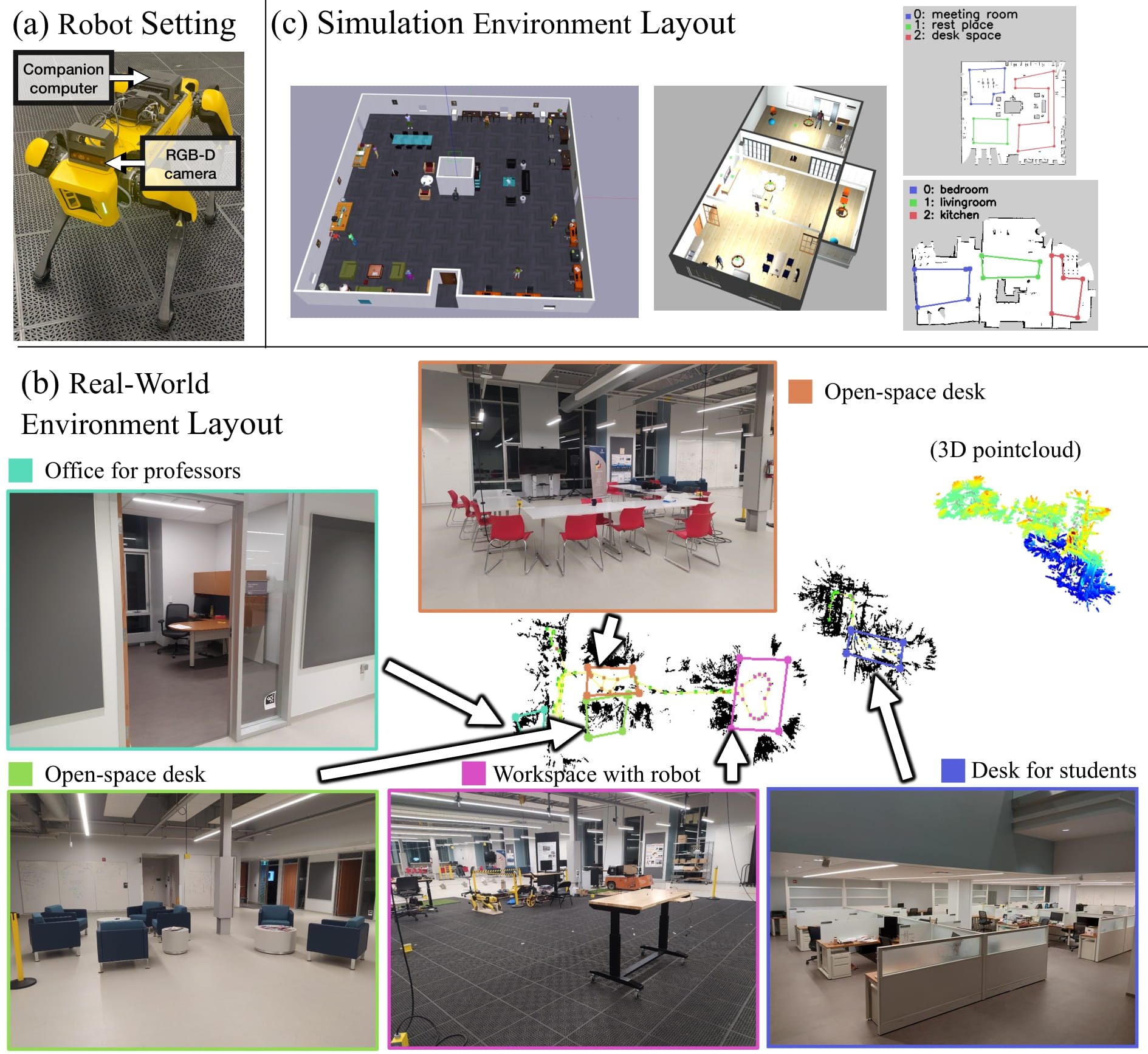
We use a Spot robot mounted with a Luxonis OAK-D-Pro camera. The real-world environment setting is a robotics lab environment, five different annotations of the floorplan are used to distinguish locations in the lab.
Search Demonstrations
Approach Demonstrations
Approach Comparison
BibTeX
@article{park2023textbased,
title={Towards Text-based Human Search and Approach with an Intelligent Robot Dog},
author={Jeongeun Park and Jefferson Silveria and Matthew Pan and Sungjoon Choi},
year={2024},
booktitle={Proc. of the International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN)},
organization={IEEE}
}